Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
- Emerging Cybersecurity Threats in the Digital Age
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cyber Defense
- The Role of Quantum Computing in Cybersecurity
- Blockchain Technology for Secure Transactions
- Zero Trust Architecture: A New Security Paradigm
- The Human Factor: Cybersecurity Awareness and Training
- Future Cybersecurity Regulations and Policies
- Conclusion
1. Introduction: The Growing Importance of Cybersecurity
In an increasingly connected world, cybersecurity has become more critical than ever. With businesses, governments, and individuals relying on digital platforms, cyber threats pose a growing risk to financial security, data privacy, and national security. The rise of sophisticated cyberattacks, including ransomware, phishing, and deepfake scams, has made it clear that traditional security measures are no longer sufficient. To combat these evolving threats, cybersecurity experts are leveraging advanced technologies and innovative strategies to protect digital assets.

2. Emerging Cybersecurity Threats in the Digital Age
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging at an unprecedented pace. Some of the biggest risks include:
- Ransomware Attacks: Cybercriminals encrypt data and demand payment for its release.
- AI-Powered Cyber Threats: Hackers use artificial intelligence to create highly convincing phishing attacks and automate cyber intrusions.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in software vendors and service providers to infiltrate multiple organizations.
- IoT Vulnerabilities: The expansion of smart devices increases attack surfaces for cybercriminals.
- Deepfake Technology: AI-generated deepfakes can manipulate public opinion and deceive individuals into security breaches.
[Insert Image Here]
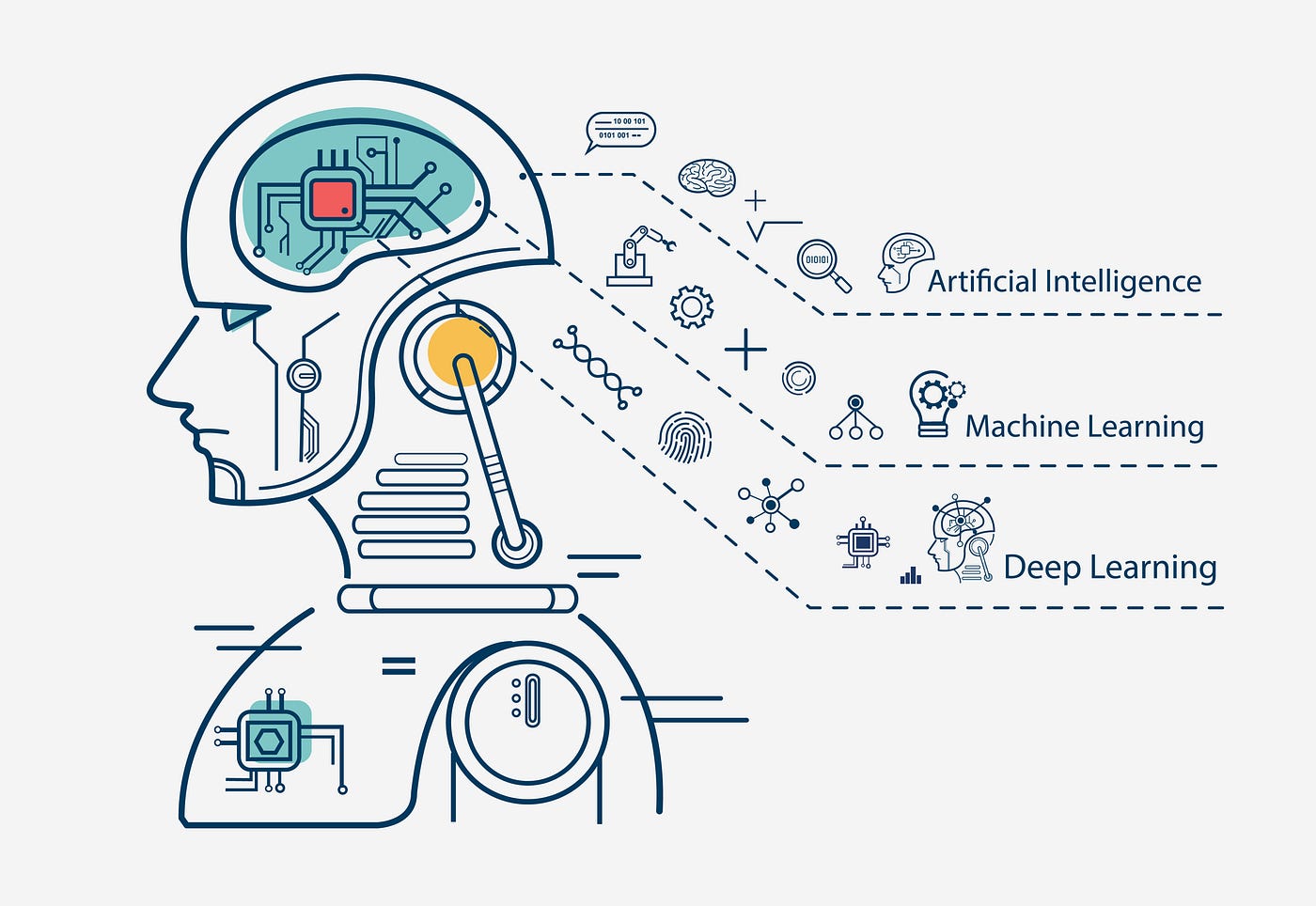
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cyber Defense
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have become essential tools in modern cybersecurity. AI-driven security systems can analyze vast amounts of data to detect anomalies, identify potential threats, and respond in real-time. Key applications of AI in cybersecurity include:
- Threat Detection and Response: AI algorithms identify unusual patterns in network traffic and flag potential threats.
- Automated Incident Response: AI can neutralize cyberattacks without human intervention.
- Fraud Prevention: Machine learning models analyze transactions to detect financial fraud and identity theft.
Despite these advantages, cybercriminals are also leveraging AI to launch more sophisticated attacks, making it crucial to develop AI-based defenses.
4. The Role of Quantum Computing in Cybersecurity
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize both cybersecurity and cyber threats. While quantum computers can break traditional encryption methods, they also offer new opportunities for ultra-secure communication. Innovations in quantum cybersecurity include:
- Quantum Encryption (Quantum Key Distribution): A method that ensures secure communication by making interception nearly impossible.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Developing encryption algorithms that can withstand quantum computing attacks.
- Quantum Random Number Generators: Enhancing encryption security by producing truly random cryptographic keys.
Organizations are investing in quantum-resistant security measures to prepare for the post-quantum era.
[Insert Image Here]
5. Blockchain Technology for Secure Transactions
Blockchain technology provides decentralized security solutions that enhance data integrity and authentication processes. Applications of blockchain in cybersecurity include:
- Secure Identity Management: Blockchain-based digital identities reduce the risk of identity theft.
- Tamper-Proof Data Storage: Blockchain records cannot be altered, ensuring data integrity.
- Decentralized Security Models: Eliminating central points of failure in authentication systems.
As blockchain adoption grows, it is becoming a critical tool for strengthening cybersecurity frameworks.
8. Future Cybersecurity Regulations and Policies
As cyber threats evolve, governments and regulatory bodies are implementing stricter cybersecurity laws to protect businesses and consumers. Some key developments in cybersecurity regulations include:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Strengthening data privacy rights for individuals.
- Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC): Ensuring defense contractors meet cybersecurity standards.
- National and International Cybersecurity Agreements: Collaborations between governments to combat cybercrime.
Organizations must stay compliant with evolving regulations to avoid legal consequences and strengthen their security posture.
[Insert Image Here]
9. Conclusion
The future of cybersecurity is filled with challenges, but also exciting innovations. From AI-driven security measures to quantum encryption and blockchain authentication, emerging technologies are reshaping digital defense strategies. However, as cybercriminals become more sophisticated, a proactive approach is necessary. By adopting Zero Trust Architecture, increasing cybersecurity awareness, and staying compliant with evolving regulations, businesses and individuals can navigate the ever-changing cybersecurity landscape with confidence.



You must be logged in to post a comment.