Table of Contents
- Understanding Website Security Threats
- What is SSL and Why is it Important?
- How to Install and Configure an SSL Certificate
- What is DDoS Protection and How Does it Work?
- Best Practices for Website Security
1. Understanding Website Security Threats
Cyberattacks are growing more sophisticated, posing significant risks to businesses. Common threats include:
- Data Breaches: Hackers steal sensitive user information.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Intercepting communication between users and websites.
- DDoS Attacks: Overloading a website with fake traffic to make it inaccessible.
A combination of SSL encryption and DDoS protection is essential for securing websites and preventing unauthorized access.

2. What is SSL and Why is it Important?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a security protocol that encrypts the communication between a user's browser and a website's server. Websites with SSL certificates display HTTPS in their URL, indicating a secure connection.
Why SSL Matters:
✅ Encrypts Data: Prevents hackers from intercepting sensitive information.
✅ Boosts SEO: Google ranks HTTPS websites higher in search results.
✅ Enhances User Trust: Users feel safer making transactions on a secure website.
✅ Prevents Phishing Attacks: Makes it harder for attackers to impersonate your website.
By implementing SSL encryption, businesses protect their users' privacy and reduce the risk of cyber threats.

3. How to Install and Configure an SSL Certificate
Securing your website with an SSL certificate involves the following steps:
Step 1: Choose the Right SSL Certificate
- Domain Validation (DV): Basic encryption for small websites and blogs.
- Organization Validation (OV): Verifies business identity and security.
- Extended Validation (EV): Highest security level for financial and e-commerce sites.
Step 2: Purchase or Obtain a Free SSL Certificate
- Paid SSL Certificates: Available from providers like DigiCert, GlobalSign, and Sectigo.
- Free SSL Certificates: Services like Let’s Encrypt offer free SSL for basic security.
Step 3: Install the SSL Certificate on Your Server
- If using cPanel, install SSL under SSL/TLS Manager.
- For cloud hosting, configure SSL through services like Cloudflare or AWS Certificate Manager.
Step 4: Update Website Links to HTTPS
- Redirect HTTP to HTTPS using .htaccess or server settings.
- Ensure third-party scripts, images, and links use secure HTTPS connections.
Once SSL is properly configured, your website becomes encrypted and safe from data interception.
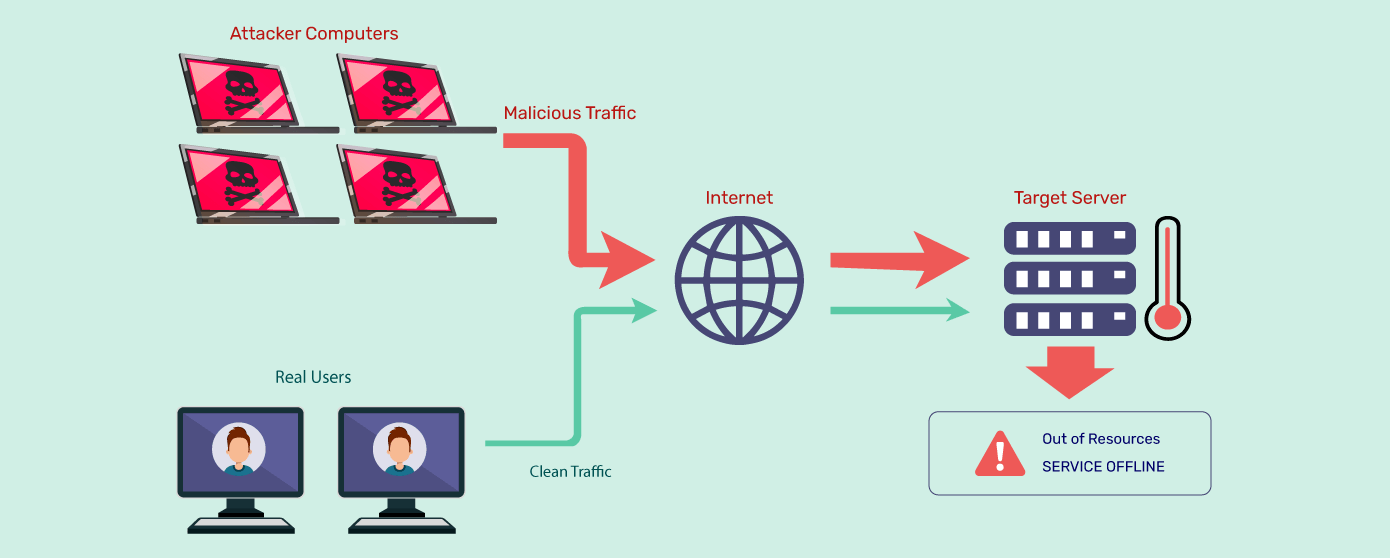
4. What is DDoS Protection and How Does it Work?
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks flood a website with fake traffic, causing downtime, slow performance, and financial loss.
How DDoS Protection Works:
- Traffic Filtering: Identifies and blocks malicious requests.
- Rate Limiting: Restricts excessive requests from suspicious IP addresses.
- Load Balancing: Distributes traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload.
- CDN (Content Delivery Network) Integration: Absorbs attacks through distributed network nodes.
Cloud-based DDoS protection services like Cloudflare, Akamai, and AWS Shield detect and mitigate attacks in real time, ensuring website availability.
5. Best Practices for Website Security
Combining SSL encryption and DDoS protection with additional security measures can further enhance website protection.
✅ Enable Web Application Firewall (WAF): Filters malicious traffic and prevents cyber threats.
✅ Use Strong Passwords & Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Reduces the risk of unauthorized logins.
✅ Keep Software & Plugins Updated: Prevents vulnerabilities in CMS platforms like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
✅ Monitor Traffic & Logs: Detects suspicious activity and potential cyber threats.
✅ Perform Regular Backups: Ensures quick recovery in case of an attack.
By implementing these security measures, businesses protect their websites, maintain trust, and ensure uptime.


You must be logged in to post a comment.