Vitamin D, commonly known as the "sunshine vitamin," plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health, supporting the immune system, and regulating mood. Despite its importance, Vitamin D deficiency has become a global health issue, affecting over 1 billion people worldwide. The lack of adequate Vitamin D can lead to a range of health problems, from bone disorders to weakened immunity and mood imbalances.
In this article, we’ll explore the common symptoms and causes of Vitamin D deficiency and provide practical solutions to help you restore and maintain optimal levels for better health.
1. Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency can often go unnoticed because its symptoms may be subtle or mistaken for other health issues. Here are the most common signs:
a. Fatigue and Low Energy
Chronic fatigue and general tiredness are some of the earliest and most overlooked symptoms of Vitamin D deficiency. Without sufficient Vitamin D, energy production in the body is compromised, leaving you feeling drained.
b. Bone and Muscle Pain
Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, a vital nutrient for strong bones. A deficiency can cause bone pain, tenderness, and even muscle cramps. Over time, this may lead to conditions like osteomalacia (softening of bones in adults) and osteoporosis.
c. Frequent Illnesses and Infections
Vitamin D plays a vital role in strengthening the immune system. Individuals with low Vitamin D levels often experience recurring infections like colds, flu, and respiratory illnesses.
d. Mood Changes and Depression
Low Vitamin D levels have been linked to mood disorders, including depression and anxiety. Vitamin D helps produce serotonin, a neurotransmitter that promotes happiness and emotional stability.
e. Hair Loss
Severe hair loss may sometimes be attributed to Vitamin D deficiency. This is because Vitamin D contributes to the creation of new hair follicles, which promote healthy hair growth.
f. Slow Wound Healing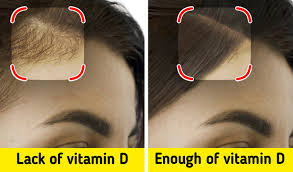
If cuts or injuries take longer to heal than usual, it could indicate insufficient Vitamin D. This vitamin helps the body reduce inflammation and promote tissue repair.
2. Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency
Understanding the causes of Vitamin D deficiency can help address the root of the problem. Here are the primary factors:
a. Limited Sunlight Exposure
The body naturally produces Vitamin D when the skin is exposed to sunlight. However, modern lifestyles often involve spending long hours indoors, reducing exposure to natural sunlight. Additionally, people living in northern latitudes receive limited sunlight during the winter months.
b. Darker Skin Tone
Melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color, reduces the skin's ability to produce Vitamin D in response to sunlight. Individuals with darker skin are therefore at a higher risk of deficiency.
c. Aging
As people age, the skin becomes less efficient at producing Vitamin D. Additionally, older adults are more likely to spend time indoors and have lower dietary intake, further increasing the risk.
d. Poor Diet
Few foods naturally contain Vitamin D, and many people don’t consume enough Vitamin D-rich foods. Common sources include fatty fish, fortified dairy products, egg yolks, and mushrooms. Vegans and vegetarians are at a higher risk due to limited plant-based options.
e. Obesity
Vitamin D is stored in fat cells, and excess body fat can prevent its release into the bloodstream. As a result, obese individuals often require higher amounts of Vitamin D to achieve healthy blood levels.
f. Medical Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, and kidney or liver disorders, can interfere with Vitamin D absorption and metabolism.
3. Solutions to Vitamin D Deficiency
The good news is that Vitamin D deficiency is preventable and treatable. Here are practical and effective solutions to restore optimal Vitamin D levels:
a. Get More Sunlight
Sunlight is the most natural way to increase Vitamin D production in the body. Aim for 15-30 minutes of sun exposure on bare skin (face, arms, and legs) at least 3-4 times a week.
Tips for Safe Sun Exposure:
Midday sun is most effective for Vitamin D synthesis.
Avoid excessive exposure to prevent sunburn and skin damage.
Individuals with darker skin may need longer sun exposure to produce sufficient Vitamin D.
b. Eat Vitamin D-Rich Foods
Incorporating Vitamin D-rich foods into your diet is a practical way to improve your levels:
Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are excellent sources of Vitamin D.
Egg Yolks: One large egg yolk contains a small amount of Vitamin D.
Fortified Foods: Many dairy products, plant-based milk, cereals, and orange juice are fortified with Vitamin D.
Mushrooms: Mushrooms exposed to sunlight or UV light can produce Vitamin D2, a plant-based form of the vitamin.
c. Take Vitamin D Supplements
For those unable to meet their needs through sunlight or diet, supplements are a reliable solution.
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol): This is the most effective form for raising blood levels.
Dosage: Consult a healthcare professional to determine the correct dosage, as needs vary based on age, weight, and deficiency levels.
d. Monitor Your Levels
A simple blood test can measure your Vitamin D levels. Aim for an optimal range of 20-50 ng/mL. Regular monitoring ensures you stay within healthy levels.
e. Lifestyle Adjustments
For those at risk of deficiency, lifestyle changes can make a significant difference:
Spend time outdoors daily.
Focus on a balanced diet with fortified and natural sources of Vitamin D.
Stay active and maintain a healthy weight to improve Vitamin D metabolism.
4. The Importance of Addressing Vitamin D Deficiency
Ignoring Vitamin D deficiency can lead to serious long-term health complications. Adequate Vitamin D levels are critical for:
Bone Health: Preventing osteoporosis, fractures, and bone softening.
Immune Support: Reducing the risk of infections, inflammation, and autoimmune disorders.
Mental Well-Being: Supporting mood stability and reducing symptoms of depression.
Overall Health: Promoting muscle strength, hair growth, and faster wound healing.
Conclusion
Vitamin D deficiency is a common yet often overlooked health issue that can significantly impact your physical and mental well-being. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and implementing simple solutions—like getting more sunlight, eating Vitamin D-rich foods, and taking supplements—you can restore and maintain optimal Vitamin D levels.
Taking control of your Vitamin D intake is a small yet powerful step toward protecting your health naturally. Start today to ensure a stronger, healthier future!


You must be logged in to post a comment.