1. Understanding Nutrition and Its Importance
Nutrition is the science of how the body uses food to sustain life, grow, and repair itself. The body requires several different nutrients to function properly, and these nutrients are typically divided into six main categories: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. Each of these nutrients plays a unique role in maintaining bodily functions.
-
Carbohydrates are the body's primary energy source. They are found in foods like grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Carbs are broken down into glucose (sugar) and provide energy for daily activities.
-
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, and are found in meat, dairy, beans, and legumes. Proteins are also important for producing enzymes and hormones that regulate bodily functions.
-
Fats are necessary for energy storage, cell function, and nutrient absorption. Healthy fats, found in sources like nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, play an essential role in brain function and hormone production.
-
Vitamins are organic compounds that the body requires in small amounts for various biochemical processes. For example, vitamin C supports immune function, while vitamin D helps with calcium absorption.
-
Minerals such as calcium, potassium, and iron are essential for building bones, transmitting nerve impulses, and oxygenating the blood.
-
Water is perhaps the most vital nutrient. It supports nearly every function in the body, from digestion and nutrient transport to temperature regulation and joint lubrication.
Each of these nutrients is crucial for maintaining good health. A deficiency in one or more can lead to health problems ranging from fatigue and weakened immunity to chronic conditions like osteoporosis or anemia.
2. The Role of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is one that provides all the nutrients the body needs in the right proportions. It typically includes a variety of foods from all food groups, ensuring that the body gets an adequate supply of essential nutrients. A balanced diet not only promotes good health but also helps maintain a healthy weight, supports brain function, and reduces the risk of developing chronic diseases such as obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.
The key to a balanced diet is variety. No single food contains all the nutrients the body requires, so eating a wide range of foods ensures that all nutrient needs are met. For example, while fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants, they may lack adequate protein. Conversely, meat, poultry, and legumes provide proteins but may be low in certain vitamins. A well-rounded diet typically includes:
-
Fruits and vegetables: These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, and should make up a large portion of your daily intake. A variety of colors in fruits and vegetables often indicates a wide range of nutrients.
-
Whole grains: Whole grains like brown rice, oats, and quinoa provide fiber, B vitamins, and minerals like iron and magnesium, which are essential for maintaining energy levels and supporting metabolic processes.
-
Proteins: A combination of plant-based and animal-based proteins, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, and nuts, ensures adequate amino acid intake necessary for muscle growth and repair.
-
Healthy fats: Including sources of unsaturated fats, like olive oil, avocado, and fatty fish (such as salmon), helps regulate cholesterol levels and supports heart health.
-
Dairy or dairy alternatives: Foods like milk, yogurt, and cheese provide calcium and vitamin D, essential for bone health.
A balanced diet doesn't mean completely eliminating any specific food group, but rather focusing on proper portions and a variety of nutrients.
3. Popular Diets and Nutritional Approaches
In recent years, various diets have gained popularity for their potential health benefits, weight management, or disease prevention. While each of these diets has its own unique guidelines, the common goal is to optimize nutrition for better health.
The Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is based on the traditional eating patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. This diet is known for its emphasis on plant-based foods, healthy fats, and moderate consumption of fish and poultry. Key components include:
- Plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes
- Healthy fats, especially olive oil
- Fish and seafood as the primary sources of protein
- Moderate intake of dairy, nuts, and seeds
Studies have shown that the Mediterranean diet is associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, and certain cancers. It is also linked to improved cognitive function and longevity.
Low-Carb and Ketogenic Diets
Low-carb diets, such as the ketogenic (keto) diet, focus on reducing carbohydrate intake to promote fat loss. The keto diet, in particular, is a very low-carb, high-fat, and moderate-protein diet that aims to shift the body's metabolism into a state called ketosis, where it burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. While these diets may help with weight loss and improved blood sugar control, they may not be suitable for everyone and should be followed under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Plant-Based Diets
A plant-based diet emphasizes whole, plant-derived foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, and nuts. It minimizes or eliminates animal products. The vegan diet, for instance, excludes all animal products, while a vegetarian diet may include dairy and eggs. A plant-based diet is linked to a lower risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. However, it is important to ensure adequate intake of nutrients typically found in animal products, such as vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern that alternates between periods of eating and fasting. There are different variations, such as the 16/8 method (fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window). This approach has been shown to support weight loss, improve metabolic health, and may increase longevity. However, it is important to approach fasting with caution, especially for those with specific health conditions.
4. The Link Between Diet and Disease Prevention
Proper nutrition plays a significant role in disease prevention and health optimization. For example, a diet high in antioxidants, fiber, and healthy fats can help reduce inflammation and lower the risk of chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease and cancer. A balanced diet also supports healthy blood sugar levels, which can help prevent type 2 diabetes.
On the other hand, poor dietary habits, such as excessive consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats, contribute to conditions like obesity, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome. These conditions can, in turn, increase the risk of developing more serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.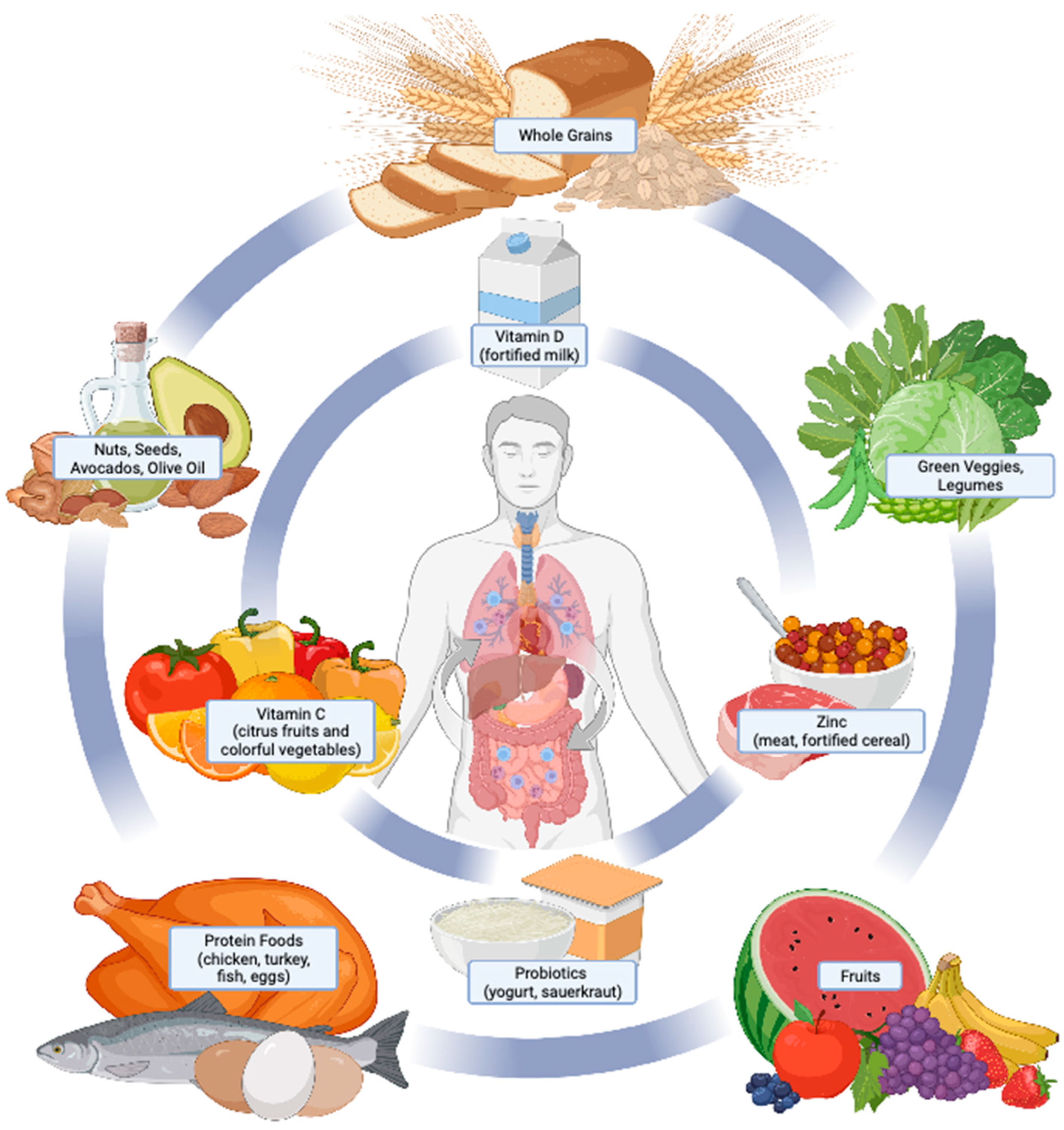



You must be logged in to post a comment.