Table of Contents
- Introduction to Christian Culture
- Core Beliefs of Christianity
- Christian Rituals and Practices
- The Role of Community in Christian Culture
- Christian Culture in Art, Music, and Festivals
- The Global Impact of Christianity
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Christian Culture
1. Introduction to Christian Culture
Christian culture is one of the most influential and diverse cultural traditions in human history. Rooted in the teachings of Jesus Christ, Christianity has shaped not only religious practices but also the values, social structures, and artistic expressions of numerous societies worldwide. Christian culture is multifaceted, encompassing a wide range of theological beliefs, rituals, and communal practices. The spread of Christianity from its origins in the Roman Empire to its current global presence has resulted in a complex cultural tapestry that reflects both unity and diversity. Christianity has been instrumental in shaping Western civilization, contributing to developments in philosophy, politics, ethics, and the arts, while also fostering rich traditions in countries across Africa, Asia, and the Americas. The essence of Christian culture lies in its message of love, salvation, and hope, values that continue to influence the lives of billions of people today.
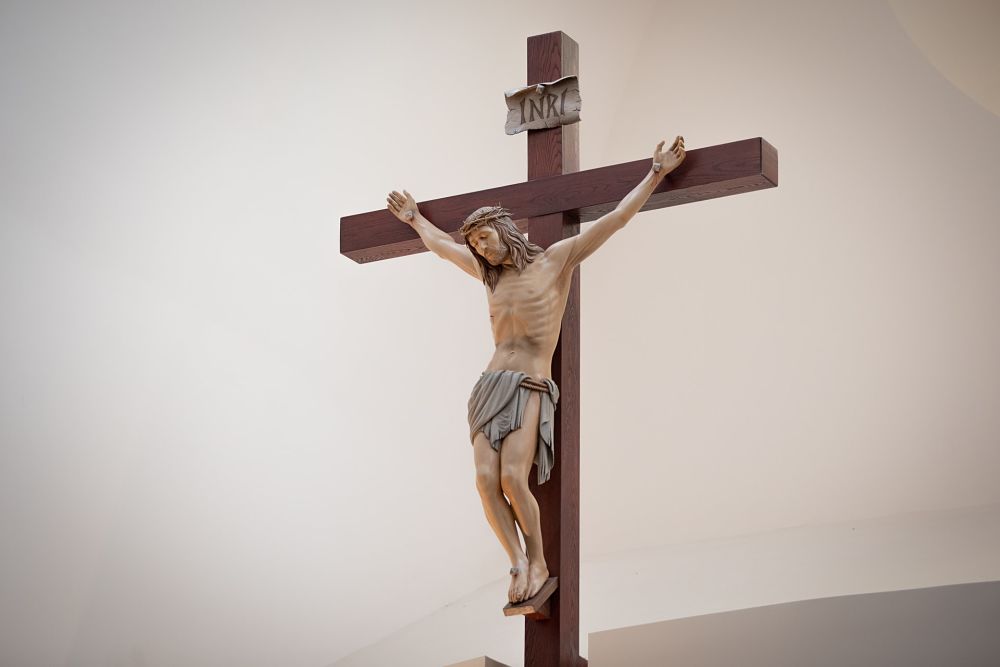

2. Core Beliefs of Christianity
At the heart of Christian culture is a set of core beliefs centered around the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians believe in the Trinity – God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ), and God the Holy Spirit – and the belief in salvation through faith in Jesus Christ. The concept of salvation, which emphasizes forgiveness of sins and eternal life, is one of the central doctrines of Christianity. Christians also adhere to the teachings of the Bible, which consists of the Old and New Testaments. The New Testament, which contains the accounts of Jesus’ life, teachings, death, and resurrection, is foundational to Christian belief. Christians believe that Jesus is the Son of God who came to Earth to redeem humanity through his sacrifice on the cross. The teachings of Jesus, including the Sermon on the Mount, focus on love, mercy, and the importance of living in harmony with one another. These beliefs form the foundation of Christian ethics and guide the moral behavior of believers worldwide.
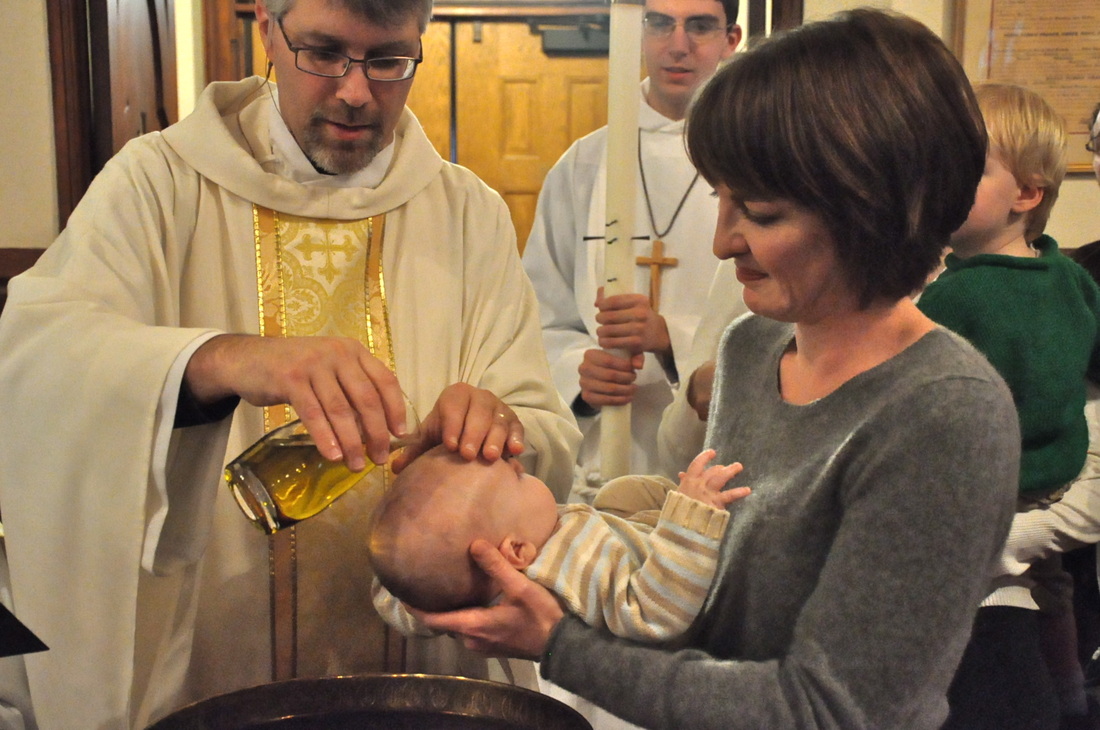
3. Christian Rituals and Practices
Rituals and practices are vital expressions of Christian faith and culture. Among the most important rituals are the sacraments, which are sacred rites that symbolize God’s grace. The two most widely practiced sacraments are Baptism and the Eucharist (also known as Communion). Baptism, typically performed with water, signifies the initiation of a person into the Christian faith. The Eucharist, in which believers partake in bread and wine, symbolizes the body and blood of Christ, commemorating the Last Supper. These rituals not only serve as acts of worship but also as means of reinforcing the community’s connection to God. Other practices in Christian culture include prayer, attending church services, and celebrating Christian holidays such as Christmas and Easter. These holidays commemorate key events in Jesus' life, such as his birth (Christmas) and resurrection (Easter), and are observed with various rituals, feasts, and cultural traditions. Christian rituals provide a sense of continuity and belonging, connecting believers across generations.
4. The Role of Community in Christian Culture
Community plays a central role in Christian culture. Christianity is not only a personal faith but also a communal practice that encourages believers to support one another and grow together in faith. The concept of the Church, both as a physical place of worship and as a spiritual community, is integral to Christian culture. The Church serves as a gathering point for worship, fellowship, and service to others. Many Christian denominations also emphasize the importance of small groups or Bible study communities, where individuals can deepen their faith and engage in fellowship. Acts of charity, such as helping the poor, visiting the sick, and providing for the needy, are key aspects of Christian community life. The New Testament emphasizes the importance of loving one’s neighbor, and this sense of community extends beyond the Church to include social justice and advocacy for the marginalized. The Christian understanding of community fosters a strong sense of belonging, shared responsibility, and mutual care.
5. Christian Culture in Art, Music, and Festivals
Christianity has had a profound impact on art, music, and cultural festivals, shaping centuries of creativity and expression. From the magnificent cathedrals of Europe to the iconography of Eastern Orthodox Christianity, Christian art has long been a medium for conveying spiritual truths and religious themes. The use of religious imagery, such as paintings of biblical scenes, statues of saints, and depictions of the Holy Trinity, is a hallmark of Christian visual culture. In music, Christian hymns, choral works, and liturgical music have become integral to worship and cultural life. Composers like Johann Sebastian Bach, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and Ludwig van Beethoven have created masterpieces inspired by Christian themes, which continue to be performed and appreciated today. Christian festivals, such as Christmas, Easter, and Pentecost, are celebrated with various customs, including feasts, processions, and music, reflecting the joy and reverence of the Christian faith. These cultural expressions help reinforce the beliefs and values of Christianity, creating a rich tapestry of worship, creativity, and celebration.
6. The Global Impact of Christianity
Christianity’s global reach has shaped not only Western societies but also cultures around the world. With an estimated 2.3 billion adherents, Christianity is the largest religion in the world. The spread of Christianity through missionary work, colonization, and migration has had a lasting influence on various cultures in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. Christianity has also played a significant role in shaping the ethical and moral frameworks of societies. Christian missionaries introduced education, healthcare, and social welfare in many parts of the world, leaving a legacy of institutions that continue to serve millions. The principles of Christianity have influenced laws, politics, and human rights movements, contributing to the development of democratic values and social justice initiatives. Despite challenges such as secularism and religious pluralism, Christianity continues to have a profound impact on global culture, offering a vision of peace, love, and reconciliation.
7. Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Christian Culture
Christian culture, with its rich tapestry of beliefs, rituals, and communal practices, continues to shape lives and societies across the globe. From its early origins to its present-day expressions, Christianity has left an indelible mark on history, influencing art, music, education, politics, and social structures. The core values of Christianity—love, compassion, and salvation—continue to resonate with people of all cultures and backgrounds, fostering a sense of hope and belonging. The enduring legacy of Christian culture is not only evident in religious practices but also in the broader cultural landscape, where its impact continues to be felt. As the world faces challenges of division and conflict, the message of Christian culture remains relevant, offering a vision of unity, peace, and reconciliation for the future.


You must be logged in to post a comment.