Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Hidden Universe
- What is Dark Matter?
- Evidence Supporting Dark Matter
- What is Dark Energy?
- The Expanding Universe and the Role of Dark Energy
- Scientific Research and Future Discoveries
1. Introduction: The Hidden Universe
The universe is vast and mysterious, filled with galaxies, stars, and planets. However, what we can see—ordinary matter—makes up only 5% of the total universe. The remaining 95% consists of two enigmatic components: dark matter and dark energy.
Dark matter was first hypothesized to explain why galaxies do not behave as expected based on visible matter alone. Meanwhile, dark energy was proposed when scientists discovered that the universe's expansion is accelerating instead of slowing down due to gravity.
Despite being invisible, these two forces shape the structure and fate of the cosmos. Scientists worldwide are working tirelessly to unravel their secrets.

2. What is Dark Matter?
Dark matter is a mysterious substance that does not emit, absorb, or reflect light, making it completely invisible to telescopes. It does not interact with electromagnetic forces like ordinary matter but has a significant gravitational influence on galaxies and cosmic structures.
Possible Candidates for Dark Matter
Scientists have proposed several possibilities for what dark matter could be:
- Weakly Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs): Hypothetical particles that interact only through gravity and the weak nuclear force.
- Axions: Extremely light particles that may explain both dark matter and quantum physics anomalies.
- Primordial Black Holes: Tiny black holes formed in the early universe that could contribute to dark matter.
Despite numerous experiments, dark matter has not been directly detected, but its presence is inferred through its effects on the universe.

3. Evidence Supporting Dark Matter
Scientists have gathered multiple lines of evidence supporting dark matter's existence.
Galactic Rotation Curves
Astronomer Vera Rubin discovered that the outer regions of galaxies rotate at unexpected speeds. According to Newtonian physics, stars at the edges of galaxies should move more slowly than those near the center. However, observations show they move at nearly the same speed—implying the presence of unseen mass providing additional gravitational pull.
Gravitational Lensing
Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that massive objects bend light. When astronomers observe this effect, they often find that the observed bending is stronger than expected based on visible matter alone. This suggests an invisible mass—dark matter—is present.
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
Data from telescopes like WMAP and Planck reveal patterns in the early universe’s radiation, indicating the gravitational influence of dark matter even in the cosmos's infancy.
Galaxy Cluster Behavior
Observations of galaxy clusters, such as the Bullet Cluster, show that mass does not align with visible matter, indicating a significant unseen component—dark matter.

4. What is Dark Energy?
While dark matter acts as cosmic glue, dark energy is an even greater mystery—it is the force driving the accelerated expansion of the universe.
In 1998, two independent research teams studying distant supernovae discovered that galaxies are moving away from each other at an increasing rate. This unexpected acceleration required a new explanation—scientists named this force dark energy.
Theories About Dark Energy
Scientists have proposed various explanations, including:
- Cosmological Constant (Λ): Einstein originally introduced this concept as a force counteracting gravity. Modern physics suggests it represents the energy of empty space itself.
- Quintessence: A dynamic energy field that changes over time, unlike a static cosmological constant.
- Modified Gravity Theories: Some researchers argue that our understanding of gravity needs to be revised at cosmic scales.
Although dark energy is a fundamental part of our current cosmological model, its exact nature remains unknown.

5. The Expanding Universe and the Role of Dark Energy
The Big Bang Theory explains that the universe has been expanding since its formation. However, scientists originally believed that gravity would slow this expansion over time. The discovery that the expansion is accelerating instead led to the Lambda Cold Dark Matter (ΛCDM) model, which divides the universe as follows:
- 70% Dark Energy – Driving expansion.
- 25% Dark Matter – Providing gravitational structure.
- 5% Ordinary Matter – The visible universe.
What Will Happen to the Universe?
The fate of the universe depends on the nature of dark energy:
- The Big Freeze: If dark energy remains constant, the universe will continue expanding until galaxies drift apart and all energy runs out.
- The Big Rip: If dark energy grows stronger, it could eventually tear apart galaxies, stars, and even atoms.
- The Big Crunch: If dark energy weakens, gravity could reverse the expansion, leading to a collapse back into a singularity.
Understanding dark energy is essential for predicting the long-term evolution of the cosmos.
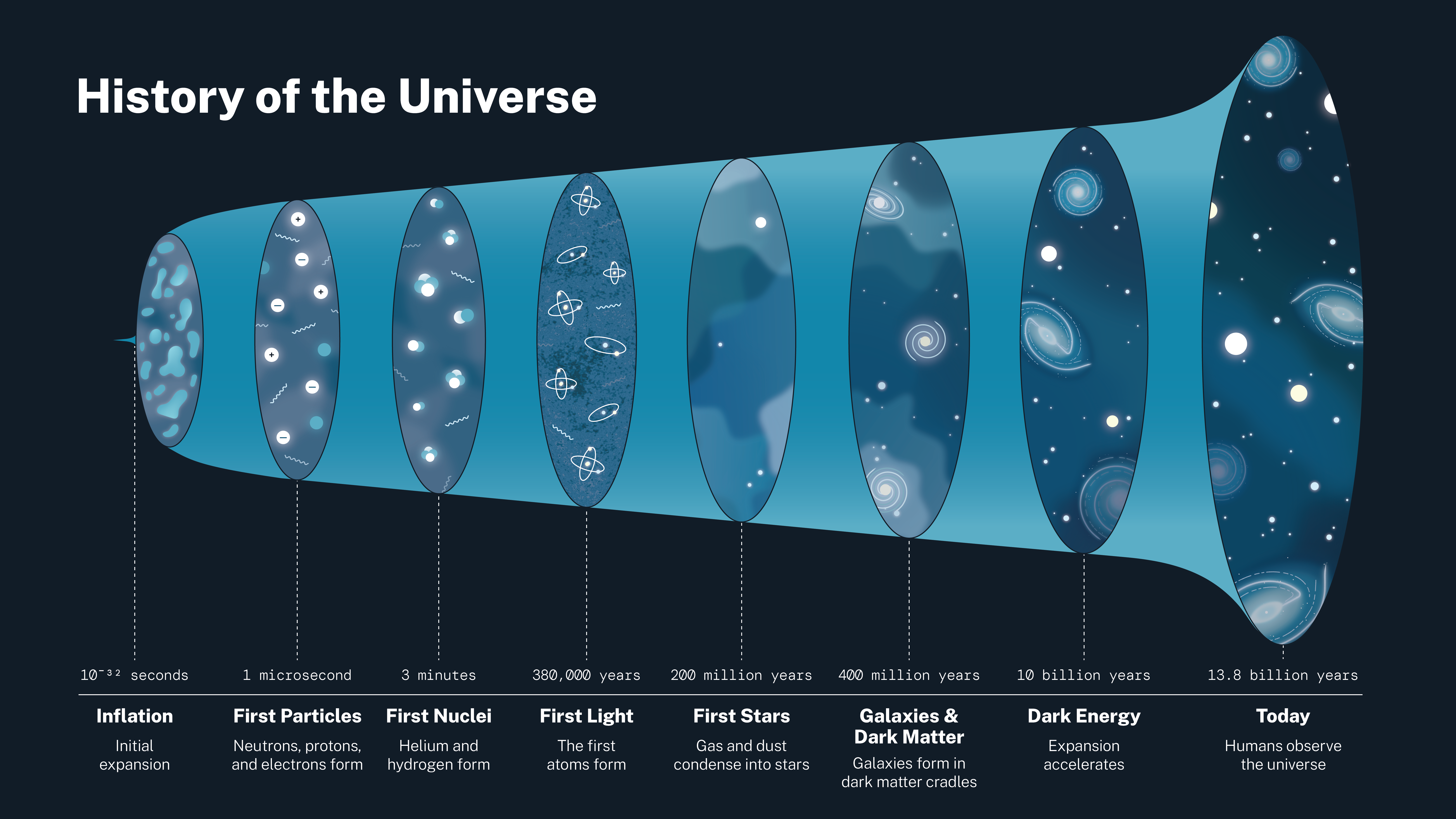
6. Scientific Research and Future Discoveries
Despite these mysteries, ongoing experiments and space missions are helping scientists learn more about dark matter and dark energy.
Dark Matter Experiments
- Large Hadron Collider (LHC): Searching for new particles that could be dark matter candidates.
- XENON and LUX-ZEPLIN Detectors: Underground labs attempting to capture dark matter interactions with ordinary atoms.
- FERMI Gamma-Ray Space Telescope: Observing potential signals from dark matter annihilation.
Dark Energy Investigations
- Euclid Space Telescope: Mapping the universe’s large-scale structure to study dark matter and dark energy.
- Vera C. Rubin Observatory: Conducting massive sky surveys to detect dark energy’s effects.
- NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope: A mission designed to analyze supernovae and gravitational lensing to better understand dark energy.
What Lies Ahead?
Dark matter and dark energy remain two of the greatest unsolved mysteries in physics. Future discoveries may revolutionize our understanding of the universe and even lead to new physics beyond Einstein’s theories.



You must be logged in to post a comment.