1. Vitamin D and Bone Health
Role in Calcium Absorption: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus, vital for strong bones.
Preventing Osteoporosis: Insufficient Vitamin D leads to weak bones, increasing osteoporosis risk, especially in older adults.
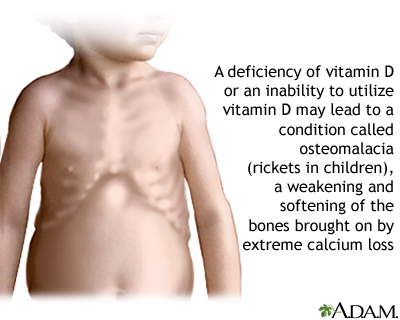
Childhood Development: Deficiency can lead to rickets in children, causing soft and weak bones.
Supporting Joint Health: Adequate levels help maintain bone density and prevent fractures.
Tips to Improve Bone Health:
Sunlight exposure (15-30 minutes daily).
Consume Vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, fortified milk, and eggs.
Consider supplements after consulting a doctor.
2. Vitamin D and Mood Regulation
Link to Mental Health: Low Vitamin D levels are associated with depression, mood swings, and Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
Brain Function: Vitamin D receptors exist in brain areas regulating mood and emotions.
Combating SAD: People in regions with limited sunlight during winter are at higher risk of SAD.
Studies and Evidence:
Research shows individuals supplementing with Vitamin D experienced mood improvements.
Improvement Tips:
Sunlight exposure boosts natural production.
Consider light therapy in winter months.
Balanced diet and supplements when needed.
3. Vitamin D and Immune Health
Strengthening Immune Response: Vitamin D enhances the pathogen-fighting capacity of immune cells (T-cells and macrophages).
Reducing Inflammation: Helps control the body’s inflammatory response to infections.
Fighting Infections: Adequate Vitamin D levels reduce the risk of respiratory infections like colds, flu, and COVID-19 complications.
Studies and Facts:
Evidence suggests people with Vitamin D deficiency are more prone to infections.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Vitamin D’s role in immune support gained attention.
Boosting Immune Health:
Combine Vitamin D with other immune-boosting nutrients like Vitamin C and Zinc.
Sunlight exposure and diet play significant roles.
4. Vitamin D Deficiency: Causes and Symptoms
Causes: Limited sun exposure, poor diet, dark skin pigmentation, obesity, and aging.
Symptoms:
Fatigue and weakness
Bone and joint pain
Frequent illness and infections
Mood changes, including depression
Who is at Risk?
Elderly individuals
People living in low-sunlight regions
Those with chronic illnesses or dietary restrictions
5. How to Maintain Healthy Vitamin D Levels
Sunlight Exposure: Aim for 15-30 minutes of sun exposure daily, especially on arms and legs.
Dietary Sources:
Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna)
Fortified dairy products and cereals
Egg yolks and mushrooms
Supplements: Vitamin D3 supplements are often recommended for those unable to get enough from sunlight or diet.
Regular Testing: Blood tests can determine Vitamin D levels and guide supplementation.
1. Vitamin D and Bone Health
- Role in Calcium Absorption: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus, vital for strong bones.
- Preventing Osteoporosis: Insufficient Vitamin D leads to weak bones, increasing osteoporosis risk, especially in older adults.
- Childhood Development: Deficiency can lead to rickets in children, causing soft and weak bones.
- Supporting Joint Health: Adequate levels help maintain bone density and prevent fractures.
Tips to Improve Bone Health:
- Sunlight exposure (15-30 minutes daily).
- Consume Vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, fortified milk, and eggs.
- Consider supplements after consulting a doctor.

2. Vitamin D and Mood Regulation
- Link to Mental Health: Low Vitamin D levels are associated with depression, mood swings, and Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
- Brain Function: Vitamin D receptors exist in brain areas regulating mood and emotions.
- Combating SAD: People in regions with limited sunlight during winter are at higher risk of SAD.
Studies and Evidence:
- Research shows individuals supplementing with Vitamin D experienced mood improvements.
Improvement Tips:
- Sunlight exposure boosts natural production.
- Consider light therapy in winter months.
- Balanced diet and supplements when needed.

3. Vitamin D and Immune Health
- Strengthening Immune Response: Vitamin D enhances the pathogen-fighting capacity of immune cells (T-cells and macrophages).
- Reducing Inflammation: Helps control the body’s inflammatory response to infections.
- Fighting Infections: Adequate Vitamin D levels reduce the risk of respiratory infections like colds, flu, and COVID-19 complications.
Studies and Facts:
- Evidence suggests people with Vitamin D deficiency are more prone to infections.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, Vitamin D’s role in immune support gained attention.
Boosting Immune Health:
- Combine Vitamin D with other immune-boosting nutrients like Vitamin C and Zinc.
- Sunlight exposure and diet play significant roles.

4. Vitamin D Deficiency: Causes and Symptoms
- Causes: Limited sun exposure, poor diet, dark skin pigmentation, obesity, and aging.
- Symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Bone and joint pain
- Frequent illness and infections
- Mood changes, including depression
Who is at Risk?
- Elderly individuals
- People living in low-sunlight regions
- Those with chronic illnesses or dietary restrictions
5. How to Maintain Healthy Vitamin D Levels
- Sunlight Exposure: Aim for 15-30 minutes of sun exposure daily, especially on arms and legs.
- Dietary Sources:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna)
- Fortified dairy products and cereals
- Egg yolks and mushrooms
- Supplements: Vitamin D3 supplements are often recommended for those unable to get enough from sunlight or diet.
- Regular Testing: Blood tests can determine Vitamin D levels and guide supplementation.

Conclusion
Vitamin D is a key nutrient that supports bone health, regulates mood, and boosts the immune system. Its deficiency can lead to serious health issues, but with proper sunlight exposure, a balanced diet, and supplements when needed, optimal levels can be maintained. Investing in Vitamin D is essential for a healthier and happier life.
1. Vitamin D and Bone Health
- Role in Calcium Absorption: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus, vital for strong bones.
- Preventing Osteoporosis: Insufficient Vitamin D leads to weak bones, increasing osteoporosis risk, especially in older adults.
- Childhood Development: Deficiency can lead to rickets in children, causing soft and weak bones.
- Supporting Joint Health: Adequate levels help maintain bone density and prevent fractures.
Tips to Improve Bone Health:
- Sunlight exposure (15-30 minutes daily).
- Consume Vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, fortified milk, and eggs.
- Consider supplements after consulting a doctor.
2. Vitamin D and Mood Regulation
- Link to Mental Health: Low Vitamin D levels are associated with depression, mood swings, and Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
- Brain Function: Vitamin D receptors exist in brain areas regulating mood and emotions.
- Combating SAD: People in regions with limited sunlight during winter are at higher risk of SAD.
Studies and Evidence:
- Research shows individuals supplementing with Vitamin D experienced mood improvements.
Improvement Tips:
- Sunlight exposure boosts natural production.
- Consider light therapy in winter months.
- Balanced diet and supplements when needed.
3. Vitamin D and Immune Health
- Strengthening Immune Response: Vitamin D enhances the pathogen-fighting capacity of immune cells (T-cells and macrophages).
- Reducing Inflammation: Helps control the body’s inflammatory response to infections.
- Fighting Infections: Adequate Vitamin D levels reduce the risk of respiratory infections like colds, flu, and COVID-19 complications.
Studies and Facts:
- Evidence suggests people with Vitamin D deficiency are more prone to infections.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, Vitamin D’s role in immune support gained attention.
Boosting Immune Health:
- Combine Vitamin D with other immune-boosting nutrients like Vitamin C and Zinc.
- Sunlight exposure and diet play significant roles.
4. Vitamin D Deficiency: Causes and Symptoms
- Causes: Limited sun exposure, poor diet, dark skin pigmentation, obesity, and aging.
- Symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Bone and joint pain
- Frequent illness and infections
- Mood changes, including depression
Who is at Risk?
- Elderly individuals
- People living in low-sunlight regions
- Those with chronic illnesses or dietary restrictions
5. How to Maintain Healthy Vitamin D Levels
- Sunlight Exposure: Aim for 15-30 minutes of sun exposure daily, especially on arms and legs.
- Dietary Sources:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna)
- Fortified dairy products and cereals
- Egg yolks and mushrooms
- Supplements: Vitamin D3 supplements are often recommended for those unable to get enough from sunlight or diet.
- Regular Testing: Blood tests can determine Vitamin D levels and guide supplementation.
Conclusion
Vitamin D is a key nutrient that supports bone health, regulates mood, and boosts the immune system. Its deficiency can lead to serious health issues, but with proper sunlight exposure, a balanced diet, and supplements when needed, optimal levels can be maintained. Investing in Vitamin D is essential for a healthier and happier life.
1. Vitamin D and Bone Health
- Role in Calcium Absorption: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus, vital for strong bones.
- Preventing Osteoporosis: Insufficient Vitamin D leads to weak bones, increasing osteoporosis risk, especially in older adults.
- Childhood Development: Deficiency can lead to rickets in children, causing soft and weak bones.
- Supporting Joint Health: Adequate levels help maintain bone density and prevent fractures.
Tips to Improve Bone Health:
- Sunlight exposure (15-30 minutes daily).
- Consume Vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, fortified milk, and eggs.
- Consider supplements after consulting a doctor.
2. Vitamin D and Mood Regulation
- Link to Mental Health: Low Vitamin D levels are associated with depression, mood swings, and Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
- Brain Function: Vitamin D receptors exist in brain areas regulating mood and emotions.
- Combating SAD: People in regions with limited sunlight during winter are at higher risk of SAD.
Studies and Evidence:
- Research shows individuals supplementing with Vitamin D experienced mood improvements.
Improvement Tips:
- Sunlight exposure boosts natural production.
- Consider light therapy in winter months.
- Balanced diet and supplements when needed.
3. Vitamin D and Immune Health
- Strengthening Immune Response: Vitamin D enhances the pathogen-fighting capacity of immune cells (T-cells and macrophages).
- Reducing Inflammation: Helps control the body’s inflammatory response to infections.
- Fighting Infections: Adequate Vitamin D levels reduce the risk of respiratory infections like colds, flu, and COVID-19 complications.
Studies and Facts:
- Evidence suggests people with Vitamin D deficiency are more prone to infections.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, Vitamin D’s role in immune support gained attention.
Boosting Immune Health:
- Combine Vitamin D with other immune-boosting nutrients like Vitamin C and Zinc.
- Sunlight exposure and diet play significant roles.
4. Vitamin D Deficiency: Causes and Symptoms
- Causes: Limited sun exposure, poor diet, dark skin pigmentation, obesity, and aging.
- Symptoms:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Bone and joint pain
- Frequent illness and infections
- Mood changes, including depression
Who is at Risk?
- Elderly individuals
- People living in low-sunlight regions
- Those with chronic illnesses or dietary restrictions
5. How to Maintain Healthy Vitamin D Levels
- Sunlight Exposure: Aim for 15-30 minutes of sun exposure daily, especially on arms and legs.
- Dietary Sources:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna)
- Fortified dairy products and cereals
- Egg yolks and mushrooms
- Supplements: Vitamin D3 supplements are often recommended for those unable to get enough from sunlight or diet.
- Regular Testing: Blood tests can determine Vitamin D levels and guide supplementation.
Conclusion
Vitamin D is a key nutrient that supports bone health, regulates mood, and boosts the immune system. Its deficiency can lead to serious health issues, but with proper sunlight exposure, a balanced diet, and supplements when needed, optimal levels can be maintained. Investing in Vitamin D is essential for a healthier and happier life.


You must be logged in to post a comment.